Proper Maintenance Planning can dramatically increase the efficiency and productivity of a maintenance team. After implementing proper planning systems, it is claimed that a Maintenance Department can perform up to 60% more work! But exactly what is Maintenance Planning, and how can it assist maintenance?
Note: This post may contain affiliate links. Please read our disclosure policy for more information.
What is Maintenance Planning?
First let’s examine the definition of Maintenance Planning.
Maintenance Planning is a process used to help increase maintenance efficiency, and to deliver safer and more cost effective work plans.
Planned Maintenance is Safer
Why is Planned Maintenance safer than Unplanned Maintenance?
Because in an unplanned situation there is usually less preparation going into hazard identification and controls. The job is more urgent and the pressure is on. This typically results in less forward planning on safety related considerations.
Planned Maintenance More Cost Effective
Why is Planned Maintenance more cost effective than Unplanned Maintenance?
Unplanned work usually requires more man-hours to execute than planned work. This is typically due to being less prepared. Overtime may be required. It may be necessary to utilise expensive experts at short notice. And it may be required to expedite parts, which carries extra costs.
Goals of Maintenance Planning
In harmony with the definition of Maintenance Planning, there are a clear set of goals for Maintenance Planning.
- Increase work team productivity by up to 60%
- Avoid time wasting maintenance delays by planning the correct resources (parts, materials, labour, equipment). Identify and address issues in advance.
- Provide a safer work environment by taking safety considerations into account when planning the job, and executing asset maintenance in a planned fashion (planned work is safer than unplanned work)
- Provide more cost effective maintenance by executing asset maintenance in a planned fashion (planned work is cheaper than unplanned work).
- Maintain the desired reliability of equipment by planning the right asset maintenance to achieve the desired level of reliability.

System of Maintenance Planning
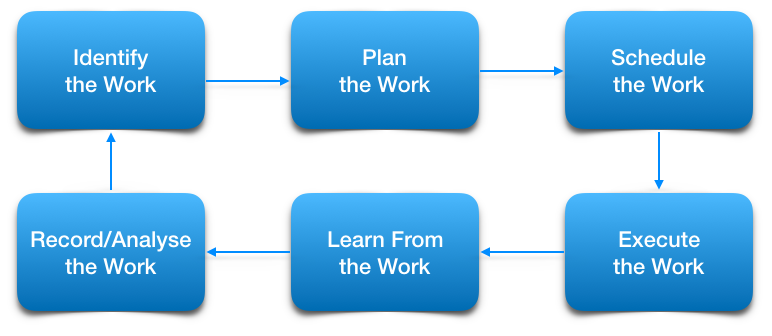
To achieve an effective Maintenance Planning System, a rigid process needs to be developed and followed. There are essentially 4 steps to the standard Maintenance Planning Process. These steps form a sustainable process of continual improvement.
- Plan the work: The What, How and Why. What is the work to be performed. How is the work to be done. Why will it be done this way?
- Do the work: Maintenance Team executes the planned and scheduled work plan.
- Learn from the job: To improve job plans and parts lists for future work.
- Record historical data: At component level for analysis and trend building, and to to assist with a cycle of continual improvement.
The following illustration adds 2 steps, identify work and schedule work. These are outside of the system of Maintenance Planning.
Periodic Maintenance Program
As part of planning the work, it is important to have a Periodic Maintenance Program in place. Also known as a Preventive Maintenance Program, or PM Program. The Maintenance Planner normally develops this program by collating job history inputs, historical data and Reliability Engineering feedback.
The result is an automated PM schedule of maintenance work with pre-defined frequencies, job procedures. Step 1 Plan the Work requires less effort as it gets automated by the CMMS.
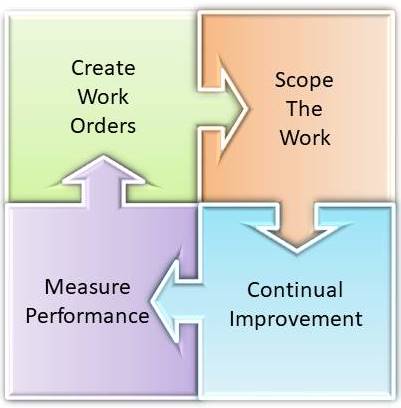
General Steps for Effective Maintenance Planning
A few general steps are required to make this Planned Maintenance system work effectively. These form the basis of the Maintenance Planner job description.
- Create Work Orders: Identify what work is required. Identify what resources (materials, tools, equipment & documents) are required to perform the work.
- Scope the Work: Provide a detailed job scope including skill requirements and time estimates.
- Continual Improvement: Improve work plans over time using feedback from work teams. Use historical data to improve standard work plans and PM program.
- Measure Performance: Measure the compliance of the work execution compared to the work plan.
Principles of Successful Maintenance Planning
To support the general steps for effective Maintenance Planning, there are some principles which should be adhered to.
- Maintenance Planners should always work independently from Maintenance Supervisors. Planners should be separated into a focused Planning Department.
- The Maintenance Planner should always focus on planning future work, not getting involved with current maintenance activities. The Asset Maintenance Team should take care of the current maintenance activities, and leave the Planning Team to focus on future work.
- Use a robust CMMS (Computerised Maintenance Management System) to manage work plans and historical data. This must be collated into equipment component levels. This necessitates Maintenance Planners with strong computer skills.
- Planner estimates job plans based on a combination of personal experience and historical work history. This means Maintenance Planners should have a well developed and relevant technical background.
- Maintenance Planners must develop strong relationships with Maintenance Supervisors, Operations and Maintenance Technicians. Maintenance Planners therefore require excellent communication skills.
- Key Performance Indicators are used to measure the success of the Planning systems. Wrench Time measured as a percentage is the standard way to measure this.
Benefits of Proper Maintenance Planning
With proper Maintenance Planning, the amount of work completed should be dramatically higher. That is, compared to the same work team without proper planning processes in place.
This means that some of the maintenance work force will be made available for other activities, thus increasing the overall productivity of the Maintenance Department.
It is indeed possible to measure this increased productivity, and thus determine the real value of Maintenance Planning.
How to Measure the Value of Maintenance Planning
The way to measure Maintenance Planning effectiveness is to measure Tool Time (a.k.a. Wrench Time). Good Maintenance Planning is understood to increase Wrench Time by up to 60%. But how can you measure Wrench Time?
Measuring Wrench Time
Wrench Time requires a standardised observation study to measure it. This requires a dedicated observer to measure workers during maintenance activities. The methodology is fairly straight forward, albeit time consuming:
- Observer is issued a standard list of work type categories and delay categories.
- A pre-determined job is allocated to the Observer to measure.
- The Observer uses a pre-determined sample time, typically 15 or 30 minutes.
- Observer records work type category or delay type category for each member of the work team at the allocated sample intervals, eg. every 15 minutes.
- At the completion of the job the Observer compiles a report for the job, calculating work times and delay times.
- The calculation is: Wrench Time = Work Time / (Work Time + Delay Time), expressed as a percentage.
- Wrench Time observations are recorded for a pre-determined number of jobs each week, and trended over time. Typically trended over months and years.
Wrench Time of 30% may be the average for an Asset Maintenance Department. In fact Wrench Time of 25% to 35% is accepted as the typical wrench time throughout a range of industries. The goal should be to increase Wrench Time by 60% through implementation of a solid Planned Maintenance System.
DIY Wrench Time Study
Here is a link to a comprehensive DIY Wrench Time Study, Quick and Easy In-House. This useful Wrench Time guide is provided by Doc Palmer, author of the definitive Maintenance Planning and Scheduling Handbook.
Maintenance Planning Affects on the Bottom Line
The truth is that effective Maintenance Planning leads to a more productive and thus more cost effective Maintenance Department. And a more cost effective Maintenance Department adds to the bottom line profit of a business. Overall there is an undeniably strong business case to implement good Maintenance Planning Processes.
Learn More about Shutdown Maintenance
There are no secrets to success. It is the result of preparation, hard work, and learning from failure. – Colin Powell
Learning from text books is one key step to enduring success. Here is some recommended reading to help you in your pursuit of excellence.
Would you like a free copy of 7 Steps to Become a KPI Ninja?
Not sure how to set up your Maintenance KPI’s? We have created the 7 Steps to Become a KPI Ninja guide to help you build, analyse and improve your KPI’s. It contains details of all the best metrics to measure, and how to interpret them. And we want you to have it for FREE.





